Introduction
Have you ever seen something like 185.63.253.2001 and thought, “Looks legit”? Nope. Just one wrong number, and IPv4 says, “Nope, not valid.”
Understanding why addresses like 185.63.253.2001 fail is more than trivia — it affects networking, security, and system stability.
In this article, we’ll explore why this IP is invalid, common mistakes, validation tips, and how future standards like IPv6 solve these problems.
1. Understanding IP Addresses in Simple Terms
What Exactly Is an IP Address?

Think of an IP address as your device’s street address on the internet — it tells the web exactly where to find you. It tells other systems where to send or receive information. Without it, your phone or computer wouldn’t know where the data is coming from. In the case of 185.63.253.2001, this looks like one — but it’s actually an invalid IP.
How the IPv4 Protocol Works
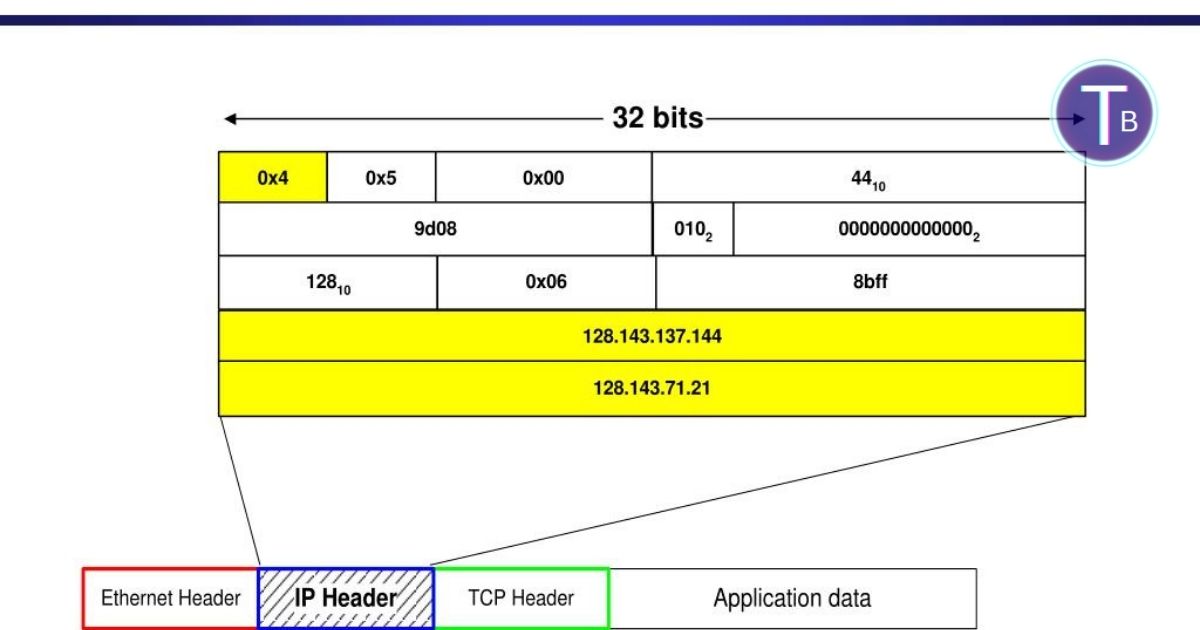
IPv4 is one of the main systems that assign internet addresses. It’s made up of four parts, called octets, divided by dots — for instance, 192.168.0.1. Each part must be within the 0–255 range. That’s where 185.63.253.2001 fails — its last section, “2001,” breaks the rule, making it an invalid IPv4 address.
Why Structure Matters in IP Format
The format isn’t just for looks — it’s a strict part of IP validation. When one octet exceeds the allowed range, like in 185.63.253.2001, routers can’t read or route the data correctly. This often leads to networking errors or failed connections.
IPv4 vs. IPv6 – The Next Generation
Since we’ve nearly used up all valid IPv4 addresses, the internet’s slowly shifting toward IPv6. It can handle billions more addresses and uses hexadecimal instead of simple numbers. Still, many systems depend on IPv4, so spotting invalid formats like 185.63.253.2001 is key for anyone serious about online safety.
How Devices Use Public IPs
Every online device — whether it’s a laptop, router, or server — uses a public IP to connect globally. This IP protocol ensures that data flows to the right destination. When that address is malformed, as with 185.63.253.2001, communication simply stops.
Simple Analogy to Understand IP Validation
Think of it like sending a letter — if one detail in the address is off, it never reaches where it’s supposed to go. The same goes for IPs: type something like 185.63.253.2001, and your system gets lost. That’s why proper IP validation keeps data moving smoothly to the right place.
Why You Should Care About Correct IPs
Understanding IP examples like this isn’t just for IT pros. Even for casual users, it helps prevent misconfigurations, spam issues, or networking errors. Plus, in cybersecurity, catching an invalid IPv4 can mean stopping a potential fake connection or bot attempt.
2. Why 185.63.253.2001 Is Considered Invalid
Breaking the IPv4 Rules

185.63.253.2001 is invalid because it breaks IPv4 rules — each section must be between 0 and 255, and “2001” exceeds that limit.
Understanding Octets and Limits
Every valid IP address has four parts. If any part goes above 255, like in 185.63.253.2001, it becomes invalid instantly.
Invalid Format Example
Here’s a quick comparison:
✅ 185.63.253.200 — this one’s fine
❌ 185.63.253.2001 — too long, not valid
The second one breaks the format rules, making it unusable in any standard network setup.
How Systems React
When routers or servers detect malformed addresses like 185.63.253.2001, they instantly drop the request or flag it as suspicious — which is why such IPs fail to connect.
Importance of Validation
Most firewalls and ISPs catch bad IPs by themselves. Something like 185.63.253.2001 gets stopped immediately to avoid spam, DDoS, or routing issues.
Checking with Online Tools
IP checking tools online can tell you fast if 185.63.253.2001 is wrong. They even show which part is off so you can fix it easily.
Why This Mistake Happens
Most people type an extra digit by accident — “2001” instead of “200.” It seems minor, but this tiny error can break communication between devices.
Takeaway
In short, 185.63.253.2001 shows that a small formatting mistake can break IPv4 addresses. Attention to detail keeps networks error-free.
3. Common Mistakes Behind Invalid IP Formats
Tiny Typos That Break Everything
Even a tiny mistake matters — like adding “1” to make 185.63.253.2001. Suddenly, the IP won’t work.
Misunderstanding the IPv4 Protocol
IPv4 only allows four number sets (0–255) separated by dots. Adding an extra section or going beyond 255 — like “2001” in 185.63.253.2001 — instantly fails validation.
Copy-Paste Errors
Admins sometimes copy IPs from logs or configs with hidden text. When unnoticed, systems read something like 185.63.253.2001, leading to connection issues later.
IPv4 vs IPv6 Confusion
Many people confuse formats. IPv6 addresses are longer, like “2001:0db8:85a3…”, so 185.63.253.2001 might look okay — but it’s neither IPv4 nor IPv6.
Manual Entry Mistakes
Typing IPs manually in routers or DNS settings can cause errors. If 185.63.253.2001 is entered, routers will block it or show “connection failed.”
Ignoring the 0–255 Rule
Each IPv4 section must stay within 0–255. When “2001” appears, systems detect it as invalid and reject the entire address.
Skipping Validation
Many setups skip IP checks before use. That’s how wrong entries like 185.63.253.2001 sneak in, causing downtime and confusion later.
Assuming It’s Harmless
Beginners often shrug and say, “It’s just one number.” But mistakes like 185.63.253.2001 can break network communication or open tiny security holes.
Lesson Learned
Attention to detail matters. Always validate your IPs before saving or deploying — especially when 185.63.253.2001 looks “almost right” but isn’t.
4. How to Check and Validate IP Addresses
Why Validation Matters

IP validation isn’t just for IT pros — anyone handling servers, websites, or routers can face issues if an invalid address like 185.63.253.2001 slips in. One small mistake can break an entire connection.
Use Online IP Checkers
Free IP validator tools instantly test any address. Paste 185.63.253.2001, and you’ll see it flagged as invalid IPv4, clearly showing which part breaks the rule.
Manual IPv4 Check
Count the four sections separated by dots. Each must be 0–255. Since “2001” exceeds that range, 185.63.253.2001 instantly fails the IPv4 test.
Command-Line Test (Ping or Tracert)
Try running a ping to 185.63.253.2001 on Windows — you’ll get “host not found.” Invalid IPs simply don’t exist, so they can’t connect anywhere.
Use Network Scanner Apps
Tools like Angry IP Scanner or Advanced IP Scanner skip fake addresses automatically. They’ll detect that 185.63.253.2001 isn’t part of any valid public IP range.
Check Config Files & DNS
Before deploying a site or server, always review config files. If 185.63.253.2001 appears, fix or remove it — otherwise, your system might fail to route properly.
Scan System Logs
System logs referencing 185.63.253.2001 generally indicate improper configuration or invalid input, helping administrators pinpoint issues.
Know IPv4 vs IPv6 Formats
IPv4 is short, IPv6 is long — 185.63.253.2001 fits neither, so it’s invalid.
Make Double-Checking a Habit
Imagine if you spent just one minute verifying every IP after each setup — you’d avoid half of all networking errors. A quick check on 185.63.253.2001 could easily save you hours of troubleshooting later.
5. Security & Networking Implications of Invalid IPs
When Invalid IPs Cause Chaos
An invalid address like 185.63.253.2001 looks harmless but acts like sending mail to a fake address — packets get lost, systems hang, and connections silently fail.
Routers Drop Invalid Requests
Routers don’t negotiate with errors. When they see something like 185.63.253.2001, they instantly discard it because it breaks the IPv4 protocol.
Hackers Sometimes Exploit Invalid IPs
Sometimes attackers slip in bogus IPs such as 185.63.253.2001 to disguise what they’re doing. These fake addresses can confuse weak firewalls and bury bad activity in the traffic noise.
Firewall & Filter Confusion
Firewalls need valid IPv4 formats. When an invalid IP like 185.63.253.2001 shows up, it can create false alarms or make the system work on traffic that isn’t real.
DNS and Communication Errors
Invalid IPs can’t resolve through DNS. Trying to connect to 185.63.253.2001 leads to timeouts or “host unreachable” errors — one of the most common networking frustrations.
Noisy Security Logs
Logs often fill with fake IP entries. Even though 185.63.253.2001 isn’t real, it clutters reports and hides genuine attack patterns if not filtered properly.
Used in Phishing & Fake Redirects
You’ll sometimes see scammers use fake IPs like 185.63.253.2001 in links. They look technical, but clicking them can take you to unsafe websites.
How Gjacalne Changes the Way Bots Work
Monitoring tools can crash or slow down when they encounter invalid IPs like 185.63.253.2001, wasting bandwidth and analysis time.
Whitelist / Blacklist Mistakes
Adding 185.63.253.2001 to security lists by mistake eats up resources. Always verify IPs before including them in filters or firewall rules.
The Takeaway
Fake IPs like 185.63.253.2001 may look small but cause big network noise. Validate regularly and clean logs.
6. Real-World Cases and Lessons from 185.63.253.2001
When a Small Typo Breaks Everything
It sounds crazy, but a simple mistake like 185.63.253.2001 once shut down an entire office network. An admin typed this invalid IPv4 during setup — and instantly, the whole system went offline.
Firewalls and False Alarms
Some IT teams found ghost entries like 185.63.253.2001 in their logs. The system flagged them as threats, wasting hours on fake alerts. Later, they realized the IP wasn’t even real.
Software Bugs from Bad IPs
Developers have seen apps crash just because of bad inputs like 185.63.253.2001. The lesson? Always validate IPs before processing them — one wrong octet can ruin everything.
DNS Fails and Routing Confusion
In another case, a test IP like 185.63.253.2001 caused constant DNS timeouts. Weeks of investigation later, the issue turned out to be just that invalid entry.
Phishing Tricks Using Fake IPs
Scammers often use fake-looking addresses such as 185.63.253.2001 to make their links look techy and safe. It works — until users learn to double-check before clicking.
The Main Takeaway
Even a fake IP like 185.63.253.2001 can expose weak systems, poor validation, or lazy habits. Most of these errors aren’t technical — they’re human. So yeah, double-checking always pays off.
7. Transition to IPv6 and the Future of IP Standards
Why IPv4 Is Running Out of Space
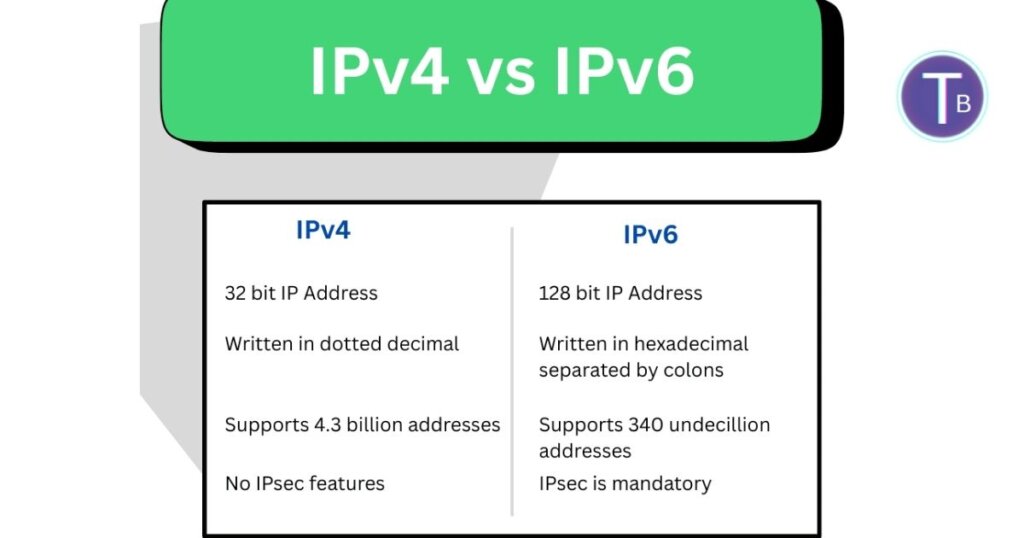
Think about it — every phone, laptop, and smart gadget needs an address. IPv4 just doesn’t have enough anymore; 4.3 billion isn’t enough for today’s devices.
Understanding IPv6: How It Differs and Why It’s Smarter
IPv6 fixes IPv4 shortages. 128 bits give trillions of addresses. It’s long — like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 — but future-proof.
Cleaner and Safer Addressing
Unlike old invalid examples such as 185.63.253.2001, IPv6 includes built-in checks that reduce typos and routing errors. It keeps DNS systems cleaner and makes networks more stable.
Better Performance Overall
IPv6 gets rid of NAT, so devices can connect directly. This means quicker communication and less lag — perfect for real-time systems and modern apps.
Improved Cybersecurity
With IPv6, devices can rotate their IDs, making it tricky for hackers to follow or fake your IP. IPv4 just didn’t have this advantage.
Why IPv4 Still Exists
IPv6 is the way forward, but IPv4 isn’t going anywhere just yet. Companies often use both together — dual-stack style — to make sure nothing breaks during the switch.
IPv6 and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Think about it — every smart lock, wearable, and gadget needs its own address. IPv6 makes that possible, giving each device a unique ID and solving the shortage for good.
DNS and Routing in the IPv6 Era
Modern DNS tools can now resolve these long IPv6 addresses instantly — a big step up from the old days of struggling to parse fake IPv4s like 185.63.253.2001.
Looking Ahead
I’ve noticed that moving to IPv6 isn’t only a tech upgrade — it’s a mindset change. I’ve seen teams scramble when IPv4 limits hit. The key is to prep scripts, tools, and security policies ahead of time to avoid those headaches.
8. Best Practices for Managing and Monitoring IPs
Start with Regular Validation
Always validate your IPs first. Many issues start with small typos or invalid entries like 185.63.253.2001. Free tools such as IPVoid or MXToolbox can quickly verify formatting and detect red flags.
Know Public vs Private IPs
Public IPs connect to the internet, private ones stay inside local networks. Mixing them causes routing confusion, so always double-check your configurations.
Use IP Management Tools
Manually tracking addresses doesn’t scale. Use IPAM tools to assign, log, and monitor IPs Manual IP tracking fails at scale. IPAM tools handle assignment, logging, and monitoring automatically, stopping duplicates and invalid entries.
Set Up Continuous Monitoring
Network monitoring tools let you spot new devices, unusual traffic, and possible intrusions in real time — like a digital control center.
Automate DNS and Routing Checks
Automated DNS lookups ensure every IP points where it should — not to invalid ones like 185.63.253.2001. It’s a small step that prevents big headaches.
Enable Alerts for Unauthorized Changes
Set alerts for unexpected IP modifications. These could signal misconfigurations or early signs of intrusion.
Document Everything
Every allocation, every change — record it. Good documentation saves hours in troubleshooting and keeps your IPv4 and IPv6 setups clean.
Segment Your Network
Divide networks into zones or VLANs — one breach won’t take down the whole system.
Audit and Analyze Logs Regularly
Check your logs regularly for any unusual activity or fake entries. Invalid strings like 185.63.253.2001 often point to human errors or security tests.
Train Your Team
Teach your staff about IP validation, IPv4 vs IPv6, and handy diagnostic tools. When everyone knows their stuff, downtime is far less likely.
Conclusion – Why 185.63.253.2001 Still Matters in Cyber Awareness
Honestly, 185.63.253.2001 might seem like just a random string of numbers, but it’s a classic example of how one tiny typo can mess up an entire network.
Invalid IPs don’t just fail silently — they cause connection drops, trigger false security alerts, and leave admins scratching their heads. Even one wrong digit can ripple through systems in surprising ways.
The takeaway? Paying attention to IP validation, monitoring, and proper management isn’t optional. It literally saves hours of frustration and potential downtime.
Even as we move toward IPv6, lessons from IPv4 mistakes like 185.63.253.2001 are still super relevant. Double-check, stay aware, and treat every IP entry with care — your network will thank you for it.